739 每日温度
题目:
给定一个整数数组 temperatures ,表示每天的温度,返回一个数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 是指对于第 i 天,下一个更高温度出现在几天后。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。
示例 1:
1
2
| 输入: temperatures = [73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73]
输出: [1,1,4,2,1,1,0,0]
|
示例 2:
1
2
| 输入: temperatures = [30,40,50,60]
输出: [1,1,1,0]
|
示例 3:
1
2
| 输入: temperatures = [30,60,90]
输出: [1,1,0]
|
提示:
1 <= temperatures.length <= 10530 <= temperatures[i] <= 100
思路
本题其实可以使用暴力解法实现的, 但是力扣的时间复杂度分析的有问题, O(n2)的时间复杂度尽然过不了。
所以只能寻求更简洁的方法, 那就是通过空间换取时间(单调栈思路)
使用单调栈, 如果出现单调递减的情况, 那么就直接入栈, 如果是递增的 ,那么就符合要求。 因为我们栈内存储的是元素的索引。 所以按照题目要求, 可以将分为2种情况讨论
因为栈内存储的是数组元素的下标索引。所以这里只需要一次for循环就可以实现,然后找出栈顶元素对应的满足要求的索引, 索引相减 即可得到我们需要的位次。
情况一:当前元素 <= 栈顶元素
- 如果当前元素 小于等于栈顶元素, 那么就直接将当前元素的索引入栈, 继续往后找 , 找到满足条件的。
情况二:当前元素 > 栈顶元素
- 如果比较得到 当前元素大于栈顶元素 ,那么这个元素就是第一个大于栈顶元素的索引, 所以直接索引相减即可得到大于栈顶元素的位次。同时将栈顶元素出栈, 栈顶出栈之后还需要对当前栈顶的元素再做判断, 万一当前栈顶的元素也满足条件呢? 所以这里就需要使用循环来进行判断。 同时最后还需要将当前元素的索引入栈。
至于更细节的图解分析。 可以看卡哥的代码随想录学习(地址 : 代码随想录 (programmercarl.com))
实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
int []res = new int[temperatures.length];
Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<>();
st.push(0);
for(int i =1 ; i < temperatures.length; i++){
if(temperatures[i] > temperatures[st.peek()]){
while(!st.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[st.peek()]){
res[st.peek()] = i - st.pop();
}
st.push(i);
}else {
st.push(i);
}
}
return res;
}
}
|
496 下一个更大元素
题目:
nums1 中数字 x 的 下一个更大元素 是指 x 在 nums2 中对应位置 右侧 的 第一个 比 x 大的元素。
给你两个 没有重复元素 的数组 nums1 和 nums2 ,下标从 0 开始计数,其中nums1 是 nums2 的子集。
对于每个 0 <= i < nums1.length ,找出满足 nums1[i] == nums2[j] 的下标 j ,并且在 nums2 确定 nums2[j] 的 下一个更大元素 。如果不存在下一个更大元素,那么本次查询的答案是 -1 。
返回一个长度为 nums1.length 的数组 ans 作为答案,满足 ans[i] 是如上所述的 下一个更大元素 。
示例 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| 输入:nums1 = [4,1,2], nums2 = [1,3,4,2].
输出:[-1,3,-1]
解释:nums1 中每个值的下一个更大元素如下所述:
- 4 ,用加粗斜体标识,nums2 = [1,3,4,2]。不存在下一个更大元素,所以答案是 -1 。
- 1 ,用加粗斜体标识,nums2 = [1,3,4,2]。下一个更大元素是 3 。
- 2 ,用加粗斜体标识,nums2 = [1,3,4,2]。不存在下一个更大元素,所以答案是 -1 。
|
示例 2:
1
2
3
4
5
| 输入:nums1 = [2,4], nums2 = [1,2,3,4].
输出:[3,-1]
解释:nums1 中每个值的下一个更大元素如下所述:
- 2 ,用加粗斜体标识,nums2 = [1,2,3,4]。下一个更大元素是 3 。
- 4 ,用加粗斜体标识,nums2 = [1,2,3,4]。不存在下一个更大元素,所以答案是 -1 。
|
提示:
1 <= nums1.length <= nums2.length <= 10000 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 104nums1和nums2中所有整数 互不相同nums1 中的所有整数同样出现在 nums2 中
进阶:你可以设计一个时间复杂度为 O(nums1.length + nums2.length) 的解决方案吗?
思路
顺着题目要求写即可, 不用使用单调栈的方式, 因为使用暴力的方法时间复杂度可能更低
实现
暴力;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int []res = new int[nums1.length];
for(int i =0 ;i < nums1.length; i++){
int j = 0;
for(; j < nums2.length; j++){
if(nums1[i] == nums2[j]){
break;
}
}
for(; j< nums2.length; j++){
if(nums2[j] > nums1[i] ){
res[i] = nums2[j];
break;
}
}
if(j == nums2.length && res[i] == 0){
res[i] = -1;
}
}
return res;
}
}
|
503 下一个更大的元素
题目:
给定一个循环数组 nums ( nums[nums.length - 1] 的下一个元素是 nums[0] ),返回 nums 中每个元素的 下一个更大元素 。
数字 x 的 下一个更大的元素 是按数组遍历顺序,这个数字之后的第一个比它更大的数,这意味着你应该循环地搜索它的下一个更大的数。如果不存在,则输出 -1 。
示例 1:
1
2
3
4
5
| 输入: nums = [1,2,1]
输出: [2,-1,2]
解释: 第一个 1 的下一个更大的数是 2;
数字 2 找不到下一个更大的数;
第二个 1 的下一个最大的数需要循环搜索,结果也是 2。
|
示例 2:
1
2
| 输入: nums = [1,2,3,4,3]
输出: [2,3,4,-1,4]
|
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
思路
就是将nums再赋值一遍, 然后找是否有大于 当前栈顶元素的元素。如果有就添加到res数组中去。但是本题我们实现的时候是通过取余的方式, 这样可以减少遍历的次数。
其实没啥差别:
实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length <= 1) {
return new int[]{-1};
}
int size = nums.length;
int []nums1 = new int[2*size];
for(int i= 0 ;i < 2*size; i++){
if(i >= size){
nums1[i] = nums[i-size];
}else{
nums1[i] = nums[i];
}
}
int[] result = new int[2*size];
Arrays.fill(result,-1);
Stack<Integer> st= new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0; i < 2*size; i++) {
while(!st.empty() && nums1[i] > nums1[st.peek()]) {
result[st.peek()] = nums1[i];
st.pop();
}
st.push(i);
}
int []temp = new int[size];
for(int i=0 ; i< temp.length; i++){
temp[i] =result[i];
}
return temp;
}
}
|
优化之后的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null || nums.length <= 1) {
return new int[]{-1};
}
int size = nums.length;
int[] result = new int[size];
Arrays.fill(result,-1);
Stack<Integer> st= new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0; i < 2*size; i++) {
while(!st.empty() && nums[i % size] > nums[st.peek()]) {
result[st.peek()] = nums[i % size];
st.pop();
}
st.push(i % size);
}
return result;
}
}
|
42 接雨水
题目:
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
示例 1:

1
2
3
| 输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
输出:6
解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
|
示例 2:
1
2
| 输入:height = [4,2,0,3,2,5]
输出:9
|
提示:
n == height.length1 <= n <= 2 * 1040 <= height[i] <= 105
思路:
本题首先我实现的思路使用暴力解法 ,虽说是暴力, 但是复杂度却是和 使用单调栈相差无几的。
根据示例1 中的这张图

首先想到的是如何计算这个雨水的面积? 横向还是纵向 ?
一个单位的雨水也就是相当于一个正方体的体积 ,我们要做的就是数正方体的个数 ,这里我们只需要考虑平面即可。同时因为横向的边长都是固定的1 , 所以这里我们通过纵向来进行计算, 也就是按照列来计算。 算出每一列的有效雨水面积,然后累加即可得到整体的面积。
通过上述的描述, 我们知道了整体的思路 ,接下来就是具体的实现思路 。
- 循环遍历每个柱子,找出每个柱子最左边 和 最右边的边界(也就是左右两边第一个比当前柱子高的柱子)
- 这里需要注意的是, 我们第一个柱子 和 最后一个柱子是不能计算的,他们充当最后的边界
- 因为我们是按列进行累加的 ,同时每个柱子的宽度都是 1 , 所以只需要算出列左右两边最短的列高 - 当前列高即可得到雨水的高。 也就可以得到雨水的体积。
实现:
上述步骤中的,第一步如果我们使用暴力解法的话, 也就是循环遍历每个柱子, 然后得到每个柱子的边界, 然后使用一个变量来接收 ,这样的作法虽然没错, 但是超时了 ,所以我们采用的是使用两个数组来接收每个柱子的边界,也同样单调栈的思路 : 通过空间换时间。 可以pass
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int[] maxLeft = new int[height.length];
int[] maxRight = new int[height.length];
int sum =0 ;
maxLeft[0] = height[0];
for(int i =1; i<height.length;i++){
maxLeft[i] = Math.max(height[i], maxLeft[i-1]);
}
maxRight[maxRight.length- 1] = height[height.length - 1];
for(int i = maxRight.length - 2 ; i>= 0; i--){
maxRight[i] = Math.max(height[i], maxRight[i+1]);
}
for(int i =0 ;i < height.length;i++){
sum += Math.min(maxRight[i], maxLeft[i]) - height[i];
}
return sum;
}
}
|
单调栈实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int sum = 0;
Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<>();
st.push(0);
for(int i = 1;i < height.length; i++){
if(height[st.peek()] > height[i]){
st.push(i);
}
if(height[st.peek()] == height[i]){
st.pop();
st.push(i);
}else{
while(!st.isEmpty() && height[st.peek()] < height[i]){
int mid = st.peek();
st.pop();
if(!st.isEmpty()){
int h = Math.min(height[i], height[st.peek()]) - height[mid];
int w = i - st.peek() - 1;
sum += h * w;
}
}
st.push(i);
}
}
return sum;
}
}
|
84 柱形图中的最大矩形
题目:
给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
示例 1:
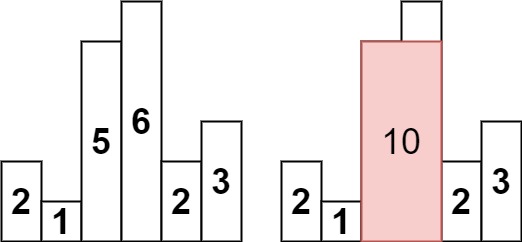
1
2
3
| 输入:heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3]
输出:10
解释:最大的矩形为图中红色区域,面积为 10
|
示例 2:
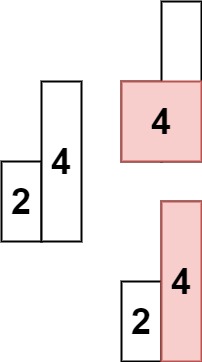
1
2
| 输入: heights = [2,4]
输出: 4
|
提示:
1 <= heights.length <=1050 <= heights[i] <= 104
思路
与上一题接雨水的 刚好相反,上题是找当前柱子的左右边界中的第一个大于 当前柱子的 。因为要接雨水,所以肯定要形成凹槽.。而本题则是找左右边界中第一个小于当前柱子高度的。 因为他要形成矩形 。所以找的就是小于当前柱子的。
所以实现思路还是和上道题是一样的,我们只需要在找边界的时候注意即可。
所以还是以空间换时间的好 ,单调栈虽然也是这个思路 ,但是所消耗的时间 和 空间都比使用数组大
实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int minLeft[] = new int[heights.length];
int minRight[] = new int[heights.length];
int sum = 0;
minLeft[0]= -1;
for(int i =1 ;i< heights.length;i++){
int t = i - 1;
while(t>= 0 && heights[t] >= heights[i]){
t = minLeft[t];
}
minLeft[i] = t;
}
minRight[minRight.length - 1] = minRight.length ;
for(int i = minRight.length - 2; i>= 0 ;i--){
int t = i + 1;
while(t <= minRight.length-1 && heights[i] <= heights[t]){
t = minRight[t];
}
minRight[i] = t;
}
for(int i =0 ;i <heights.length; i++){
int weight = minRight[i] - minLeft[i] -1;
int height = heights[i];
sum = Math.max(sum, weight * height);
}
return sum;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int [] newHeights = new int[heights.length + 2];
newHeights[0] = 0;
newHeights[newHeights.length - 1] = 0;
for (int index = 0; index < heights.length; index++){
newHeights[index + 1] = heights[index];
}
heights = newHeights;
int res = 0 ;
Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<>();
st.push(0);
for(int i =1; i < heights.length ;i++){
if(heights[st.peek()] < heights[i]){
st.push(i);
}if(heights[i] == heights[st.peek()]){
st.pop();
st.push(i);
}else{
while(!st.isEmpty() && heights[st.peek()] > heights[i]){
int mid = st.pop();
if(!st.isEmpty()){
int left = st.peek();
int right = i;
int w = right - left - 1;
int h = heights[mid];
res = Math.max(res, w * h);
}
}
st.push(i);
}
}
return res;
}
}
|










