题40.组合总和三
给定一个候选人编号的集合 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用 一次 。
注意:解集不能包含重复的组合。
示例 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| 输入: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
输出:
[
[1,1,6],
[1,2,5],
[1,7],
[2,6]
]
|
示例 2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| 输入: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5,
输出:
[
[1,2,2],
[5]
]
|
思路
首先根据我们之前的总结,可以确定这道题我们需要到回溯
【回溯可以解决的问题 :
- 组合问题:N个数里面按一定规则找出k个数的集合
- 切割问题:一个字符串按一定规则有几种切割方式
- 子集问题:一个N个数的集合里有多少符合条件的子集
- 排列问题:N个数按一定规则全排列,有几种排列方式
- 棋盘问题:N皇后,解数独等等
】
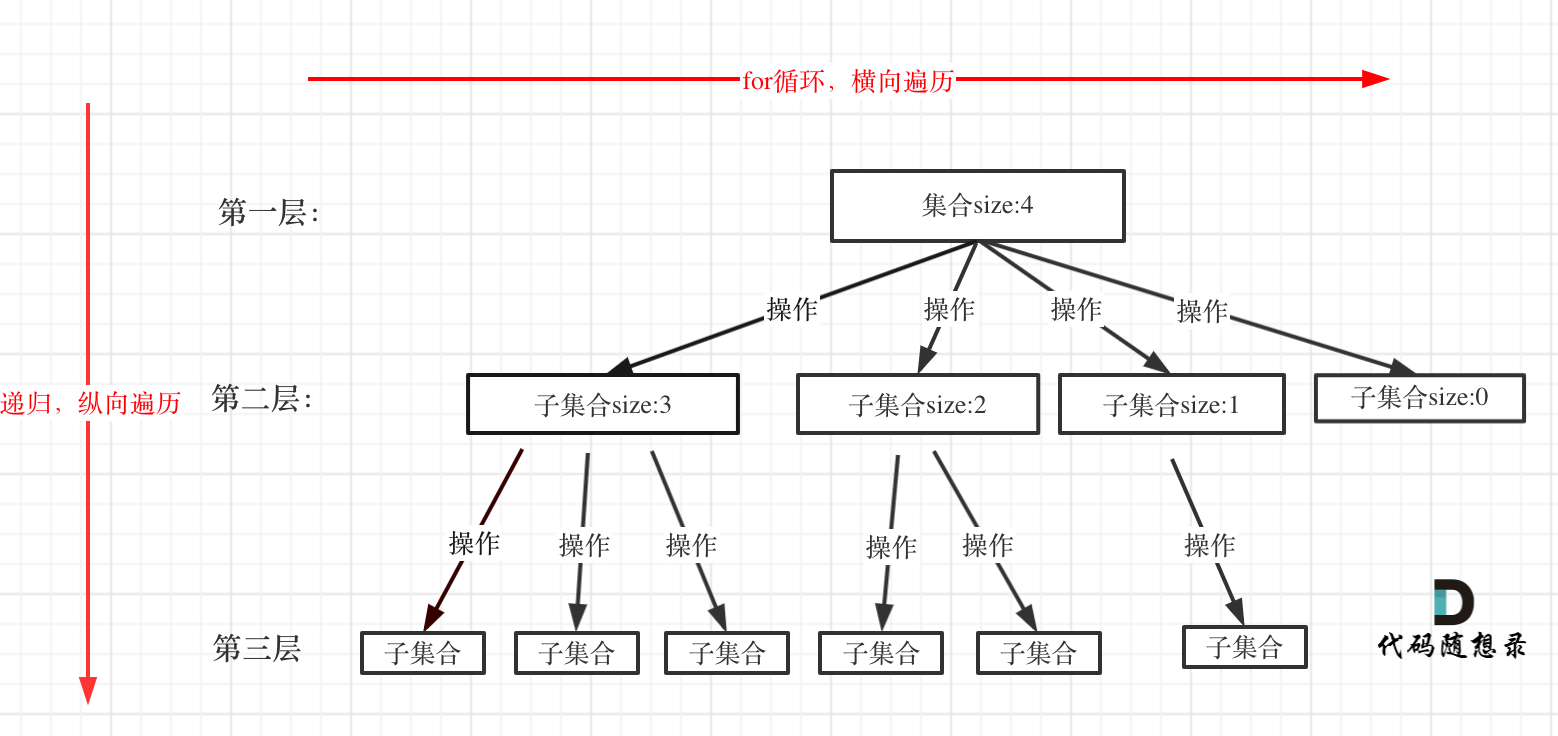
如果按照我们之前的思路,那么这道题就是经典的递归回溯三部曲,[参考上面的图示]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| void combine(XXX,XXX ,xxx){
for(....){
}
}
|
大致思路基本就是这样的。
但是: 这道题中有一个很重要的条件
所以:在使用递归解决时我们就必须得注意
实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
if(candidates.length == 0){
return res;
}
Arrays.sort(candidates);
combine(candidates,target,0,0);
return res;
}
public void combine(int[] nums,int target,int sum ,int index){
if(sum == target){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = index; i <nums.length ;i++){
sum += nums[i];
combine(nums,target,sum,i+1);
sum -= nums[i];
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}
|
如果按照这样做出来,那么对于平常的组合问题是没有问题得,但是这道题中得限制条件却不能满足
注意:解集不能包含重复的组合。
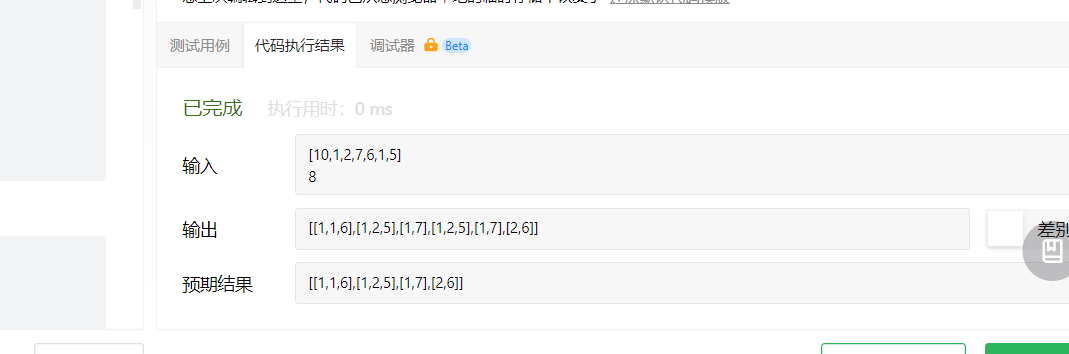
由此我们可以看出他是无法满足我们设置的必要条件的,
改进思路
- 先对数组进行排序,让相同的元素放在相同的位置
- 然后使用如果前后两个元素相同,那么就将后面相同的元素跳过
1
2
3
| if(i > index && nums[i] == nums[i-1] ){
continue;
}
|
这样我们就可以保证所有相同的元素中只有一个1 进入了循环
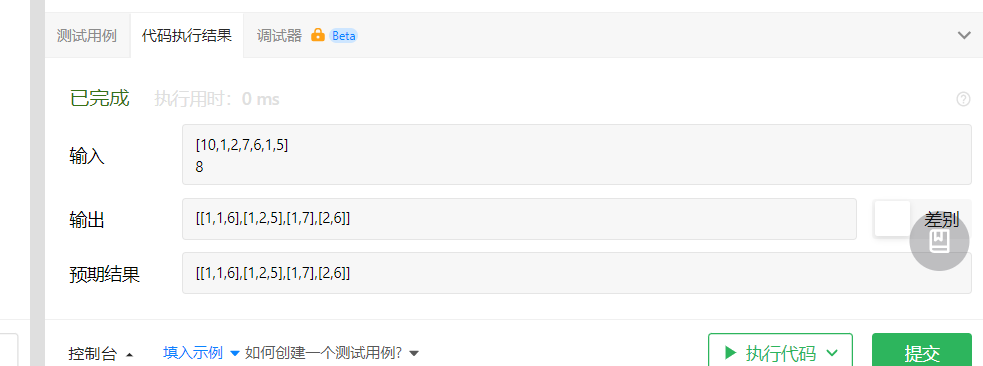
优化三
如果按照之前的解法,我们就必须将所有的元素都进行相加,判断。如果这样那么效率就会大大降低
对于那些没有用的元素我们其实可以不进行相加的,在for循环判断时就可以剃齿多余的运算,从而节省效率
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| package day11;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
if(candidates.length == 0){
return res;
}
Arrays.sort(candidates);
combine(candidates,target,0,0);
return res;
}
public void combine(int[] nums,int target,int sum ,int index){
if(sum == target){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = index; i <nums.length && sum + nums[i] <= target;i++){
if(i > index && nums[i] == nums[i-1] ){
continue;
}
sum += nums[i];
combine(nums,target,sum,i+1);
sum -= nums[i];
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}
|
相关图片取自代码随想录,题目来源力扣40
题131.分割回文串
给你一个字符串 s,请你将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是 回文串 。返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。回文串 是正着读和反着读都一样的字符串。
示例 1:
1
2
| 输入:s = "aab"
输出:[["a","a","b"],["aa","b"]]
|
示例 2:
1
2
3
4
5
| 输入:s = "a"
输出:[["a"]]
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 16
s 仅由小写英文字母组成
|
思路 + 实现
【分割】 从这一关键字中我们就可以看出这种类型的题需要用到递归回溯算法
【分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是 回文串 。】那么我们就需要实现方法判断是不是回文串
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public boolean isVir(String str ,int start ,int end){
for(int i =start ,i <= end ; i++,end--){
if(str.charAt(i) != str.charAt(end)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
|
然后回归到这道题本身,那么就可以判断是否子串是回文串了
接下来就是实现递归回溯的思路(递归三部曲)
- 确定递归函数的参数、返回值
1
2
3
| public void combine(String str , int index){
}
|
- 确定递归终止的条件
1
2
3
4
| if(index >= str.length()){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
|
- 单层递归回溯的逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| for(int i = index , i < s.length();i++){
if(isVir(s,index , i)){
String str = s.substring(s,index,i + 1);
path.add(str);
}else{
continue;
}
combine(s,i+1);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
|
实现版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| class Solution {
public List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
if(s.length() == 0){
return res;
}
combine(s,0);
return res;
}
public void combine(String str , int index){
if(index >= str.length()){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = index; i < str.length() ;i++){
if(isVir(str,index,i)){
String s1 = str.substring(index ,i + 1);
path.add(s1);
}else{
continue;
}
combine(str,i+1);
path.remove(path.size()- 1);
}
}
public boolean isVir(String str , int start ,int end){
for(int i =start;i < end;i++,end--){
if(str.charAt(i) != str.charAt(end)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
|
有效 IP 地址 正好由四个整数(每个整数位于 0 到 255 之间组成,且不能含有前导 0),整数之间用 '.' 分隔。
- 例如:
"0.1.2.201" 和 "192.168.1.1" 是 有效 IP 地址,但是 "0.011.255.245"、"192.168.1.312" 和 "192.168@1.1" 是 无效 IP 地址。
给定一个只包含数字的字符串 s ,用以表示一个 IP 地址,返回所有可能的有效 IP 地址,这些地址可以通过在 s 中插入 '.' 来形成。你 不能 重新排序或删除 s 中的任何数字。你可以按 任何 顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
1
2
| 输入:s = "25525511135"
输出:["255.255.11.135","255.255.111.35"]
|
示例 2:
1
2
| 输入:s = "0000"
输出:["0.0.0.0"]
|
示例 3:
1
2
| 输入:s = "101023"
输出:["1.0.10.23","1.0.102.3","10.1.0.23","10.10.2.3","101.0.2.3"]
|
思路 + 实现
首先我们可以确定有效ip的逻辑
- 段位以0为开头的数字不合法
- 段位里有非正整数字符不合法
- 段位如果大于255了不合法
满足以上三点就可以作为有效ip
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public boolean isVir(String str,int start ,int end){
if(start > end){
return false;
}
if(str.charAt(start) == '0' && start != end){
return false;
}
int tmep = 0;
for(int i = start; i <= end;i++){
if(str.charAt(i) < '0' || str.charAt(i) > '9'){
return false;
}
tmep = 10 * tmep + (str.charAt(i) - '0');
if(tmep > 255){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
|
接下来就是递归回溯三步
1
2
3
4
|
public void combine(String s ,int index,int number){
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
if(number == 3){
if(isVir(s,index,s.length())){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
return;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| for(int i = index; i < s.length();i++){
if(isVir(s,index,i)){
s = s.substring(0,i+1) + "." + s.substring(i+1);
path.add(s);
number++;
combine(s,i+2,umber);
number--;
s = s.substring(0, i + 1) + s.substring(i + 2);
}else{
break;
}
}
|
最终实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| class Solution {
public List<String > res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
if(s.length() < 4 || s.length() > 12){
return res;
}
combine(s,0,0);
return res;
}
public void combine(String s ,int index,int number){
if(number == 3){
if(isVir(s,index,s.length() - 1 )){
res.add(s);
}
return;
}
for(int i = index;i < s.length();i++){
if(isVir(s,index,i)){
s = s.substring(0,i + 1) + '.' + s.substring(i + 1);
number++;
combine(s,i+2,number);
number--;
s = s.substring(0, i + 1) + s.substring(i + 2);
}else{
break;
}
}
}
public boolean isVir(String str,int start ,int end){
if(start > end){
return false;
}
if(str.charAt(start) == '0' && start != end){
return false;
}
int tmep = 0;
for(int i = start; i <= end;i++){
if(str.charAt(i) < '0' || str.charAt(i) > '9'){
return false;
}
tmep = 10 * tmep + (str.charAt(i) - '0');
if(tmep > 255){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
|








