题目
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数

使用前序(中左右),也可以使用后序遍历(左右中),使用前序求的就是深度,使用后序求的是高度。
对于二叉树最大深度和最大高度的理解
- 二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
- 二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
而根节点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度,所以本题中我们通过后序求的根节点高度来求的二叉树最大深度。
递归法: (三部曲)
- 递归法传参是重点
1
2
|
int getDepth(Node root);
|
- 递归的终止条件就是判断是否为叶子节点(也就是说如果下一个节点为空的话就返回 0 )
1
2
3
| if(node == null){
return 0;
}
|
- 确定单层递归的逻辑
思路
确定单层递归的逻辑:先求它的左子树的深度,再求右子树的深度,最后取左右深度最大的数值 再+1 (加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的树的深度。
代码实现
1
2
3
| int leftDepth = getDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = getDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth,rightDepth) + 1;
|
对于递归的题。个人感觉最好将其从题目中提取出来,因为返回值的考虑会让我们分心去思考这样递归是否会超出范围等等,所以将有返回值的递归题 提取成为一个方法是最好的做法!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class Solution {
int result = 1;
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
getDepth(root,result);
return result;
}
public void getDepth(TreeNode root , int deep){
result = deep > result ? deep:result;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
return;
}
if(root.left != null){
getDepth(root.left,deep+1);
}
if(root.right != null){
getDepth(root.right,deep+1);
}
}
}
|
迭代法
对于这种求解深度的问题来说,使用迭代法相较来说是比较麻烦的,因为我们需要一层一层的遍历,最后得到的层数就是最大的深度。
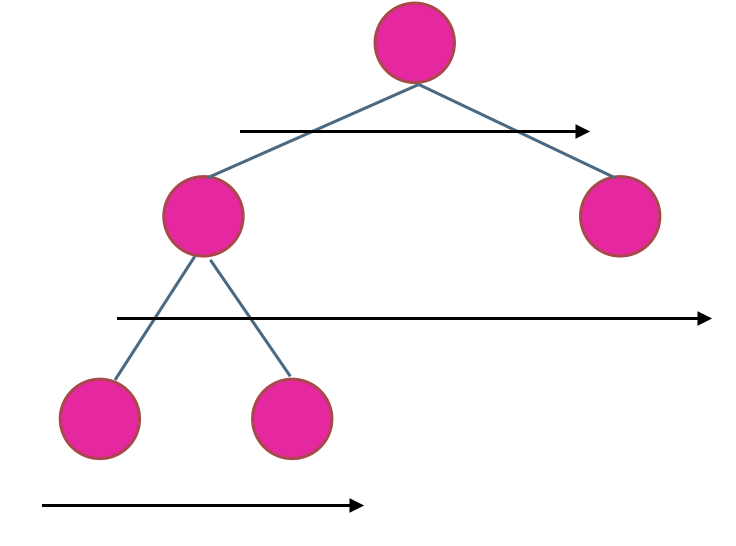
思路
层序遍历每一次计算队列的长度时(也就是当前层的元素全部在队列中的时候)。此时将层数加1,然后将整棵树遍历完后,得到的二叉树的层数就是我们需要的最大深度
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int dept = 0;
Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root);
while(!que.isEmpty()){
dept++;
int size = que.size();
for(int i =0 ;i<size;i++){
TreeNode node = que.poll();
if(node.left != null){
que.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
que.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return dept;
}
}
|
同类型的对于N叉树的最大深度
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| class Solution {
int result = 1;
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
getDepth(root,result);
return result;
}
public void getDepth(Node root, int deep){
result = Math.max(deep,result);
for(int i =0 ;i< root.children.size();i++){
getDepth(root.children.get(i),deep+1);
}
}
}
class solution {
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int depth = 0;
Queue<Node> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(root);
while (!que.isEmpty())
{
depth ++;
int len = que.size();
while (len > 0)
{
Node node = que.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < node.children.size(); i++)
if (node.children.get(i) != null)
que.offer(node.children.get(i));
len--;
}
}
return depth;
}
}
|
二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 从根节点开始 ,那么就是说如果根节点的左右子节点如果有一个为空的话那么就不能算
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

思路
和求最大深度有些类似,但是也有很多不同
思路就是 : 如果左子树为空,右子树不为空,说明最小深度是 1 + 右子树的深度。
反之,右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是 1 + 左子树的深度。 最后如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树深度最小值 + 1 。
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = minDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = minDepth(root.right);
if (root.left == null) {
return rightDepth + 1;
}
if (root.right == null) {
return leftDepth + 1;
}
return Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int size = deque.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode poll = deque.poll();
if (poll.left == null && poll.right == null) {
return depth;
}
if (poll.left != null) {
deque.offer(poll.left);
}
if (poll.right != null) {
deque.offer(poll.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
}
|
求最小深度推荐用迭代法实现
| 提交结果 |
执行用时 |
内存消耗 |
语言 |
提交时间 |
备注 |
| 通过 |
1 ms |
60.2 MB |
Java |
2023/01/18 15:04 |
迭代 |
| 通过 |
9 ms |
61.5 MB |
Java |
2023/01/18 15:03 |
递归 |










